#
Learnbot – Emotion Recognition
(Idea Proposal)
## MASKING - FACS - AUs – XGBOOST (2-fold and 1-full classifier)
### Aim Of Model:
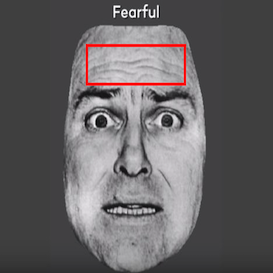
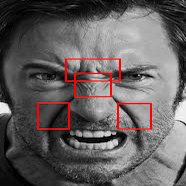
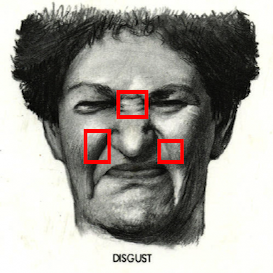
Our aim is to recognize the emotions of humans examining their facial expressions and classify them into various emotion classes. The software should distinguish emotions among 5 of 6 different classes. They are ‘happy’, ‘sad’, ‘fear’, ‘disgust’ and ‘angry’ along with neutral state.
The model should recognize the emotions in real – time and should be very fast.
It should recognize emotions by performing moderate computations (no complex computations like DNNs) but should be very accurate.
The emotions of a person to be recognized can possess various poses of the face and the structure of face may differ from one another.
### Features:
- **--** Derives face pose angle.
- **--** Frontal face view to Profile face view recognition.
- **--** Least preprocessing requirement.
- **--** Real-time recognition.
- **--** Moderate computations performed.
- **--** Face skin texture examined
- **--** Fastest and Accurate Classifier: Xgboost.
- **--** 2-fold and 1-full classifier increase prediction accuracy.
### Hardware Requirements:
**Camera Module:**
- **--** 30 FPS
- **--** 3 MPixels
**CPU System:**
- **--** Processor 1.6 GHz base frequency.
- **--** 2 GB RAM
- **--** Quad Core
- **--** 32 GB Memory
**Raspberry Pi 3 model**
- **--** Video streaming via RPi_Cam_Web_Interface
Minimum of above should be met for the trained model to be executed.
### Software Requirements for Model:
OpenCV, Python, Xgboost, Numpy, Matplotlib, imutils, Sckilite
### Technologies and algorithms used:
HOG LBP cascades, Gabor LBP cascades, facial landmarks AAM, face Golden Ratio modeling, Action Units (AUs), Facial Action Coding System(FACS), Xgboost, etc.
##
### Action Units (AUs) and Facial Action Coding System (FACS):
Emotion expressions on a face are possible due to movement of various facial muscles. The Facial Action Coding System (FACS) refers to a set of facial muscle movements that correspond to a displayed emotion. It is an anatomical system for describing all observable facial movements into small units known as Action Units (AUs). AUs determines activeness of different sets of facial muscles at a time.
### Xgboost:
XGBoost (Extreme Gradient Boosting) is an optimized distributed gradient boosting algorithm. The algorithm is designed to work with numeric values only. It is also known as ' **regularized boosting**' technique because of its techniques to reduce overfitting problem automatically even with less training data.
The performance of xgboost is recorded to be more than other famous algorithms like DNN, random forest, etc. It is faster than other algorithms as it implements parallel processing.It helps to correct errors made by previously trained tree thus. Moreover, it allows defining custom optimization objectives and evaluation criteria. We can even start training an XGBoost model from its last iteration of the previous run, which makes training simpler.
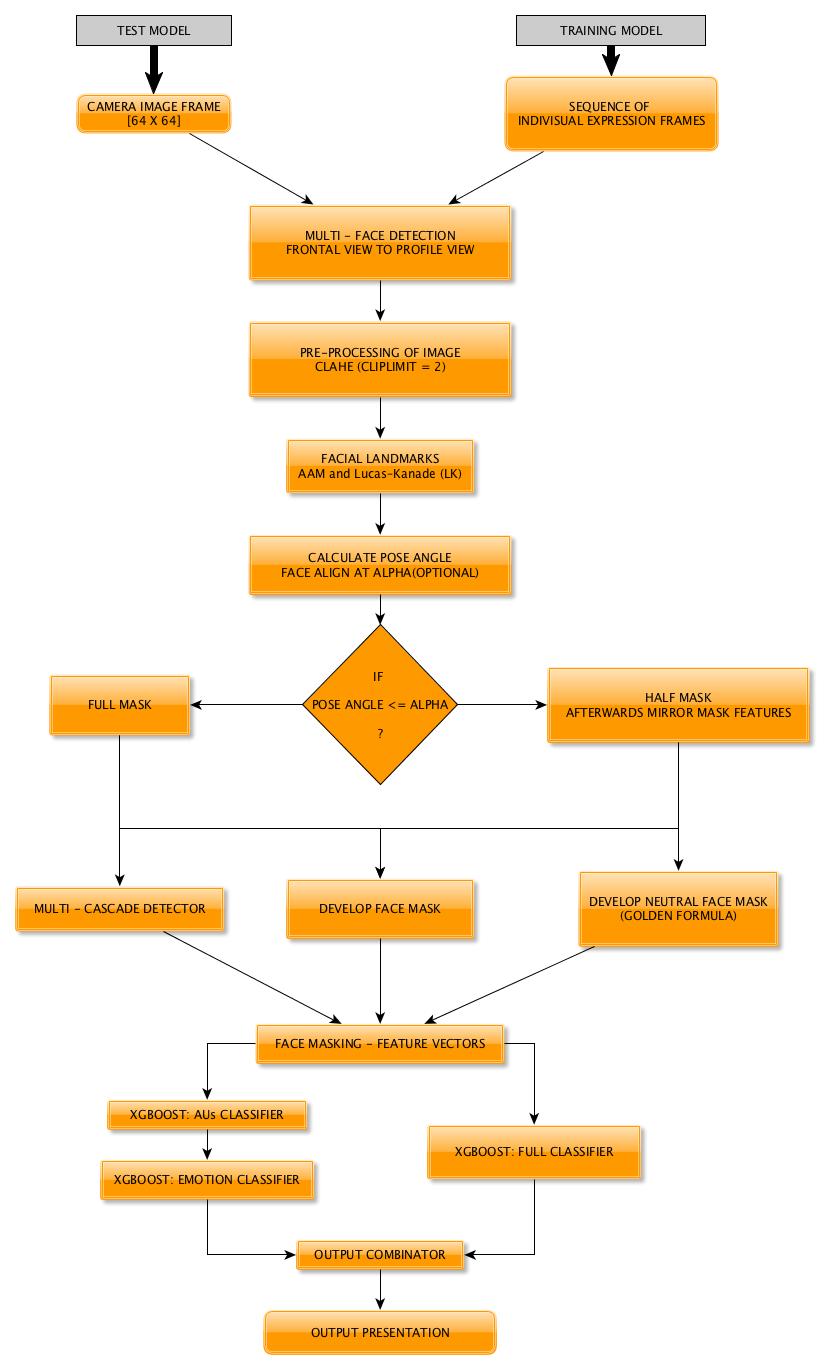
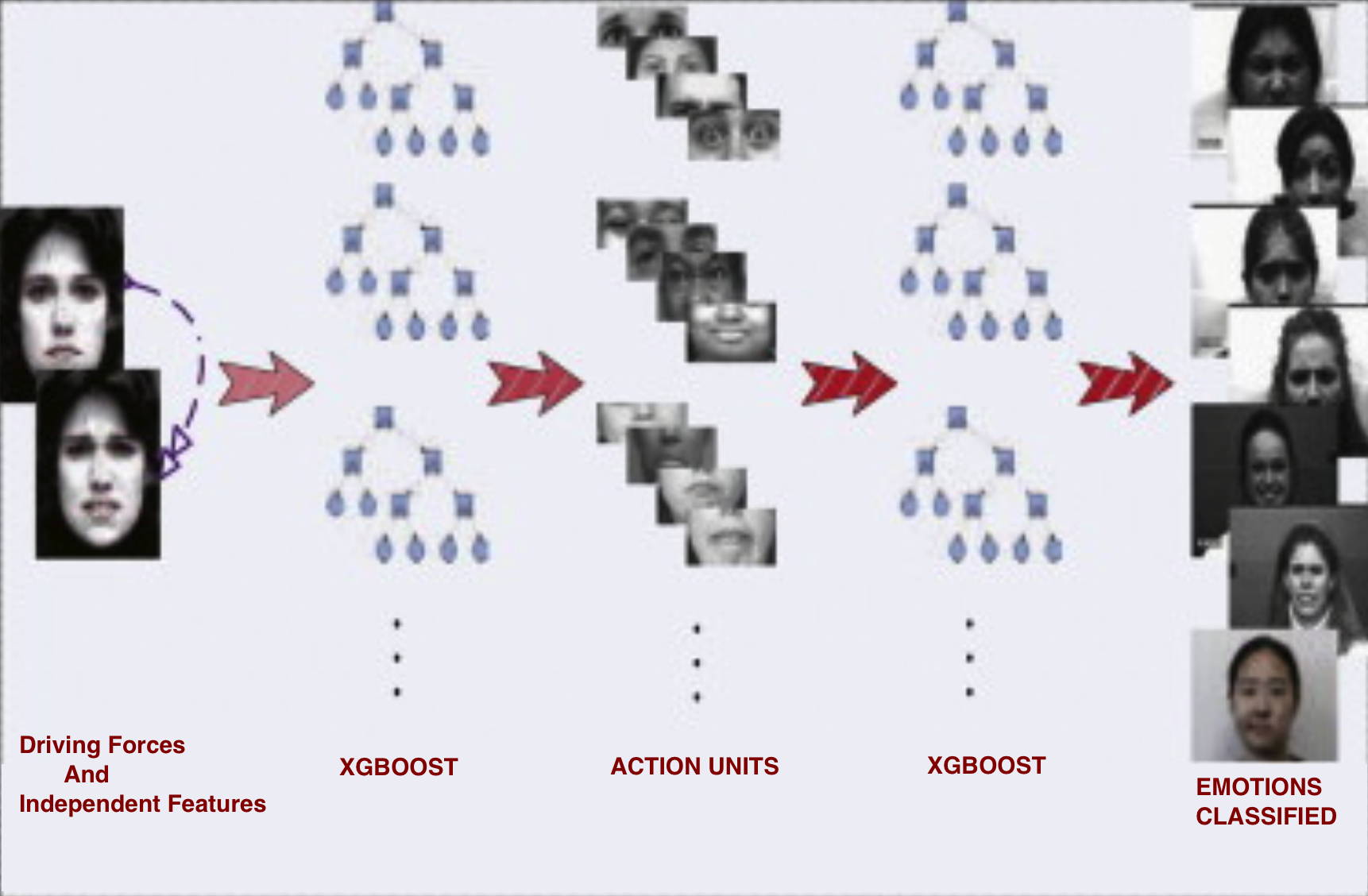
## Flowchart:
## Overview:
The model can be implemented for emotions recognition of human face captured by Learnbot's camera module. The model computes moderate operations and performs in real time with sufficient frames per seconds. It performs suitable processes parallel in order to reduce the runtime.
During the training phase, the model takes the inputs in the form of a sequence of frames of each expression. This helps to classify the emotions accurately even with less expression intensity. During runtime, the model is fed with captured images by Learnbot's camera module in real time. The model is designed such that it requires least **pre-processing** and **face –alignment**. This reduces run-time and increases the accuracy of further processes.
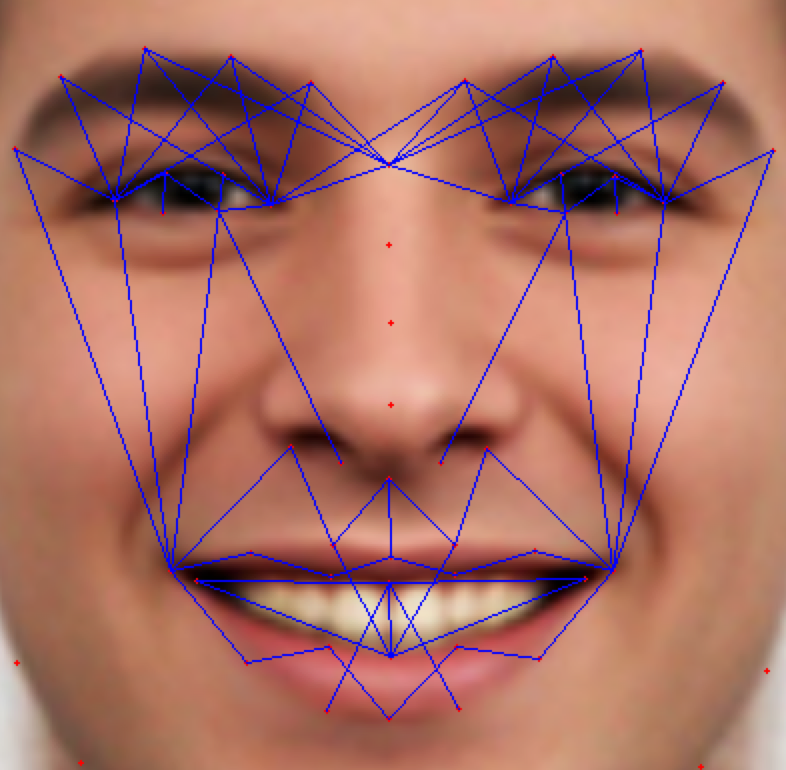
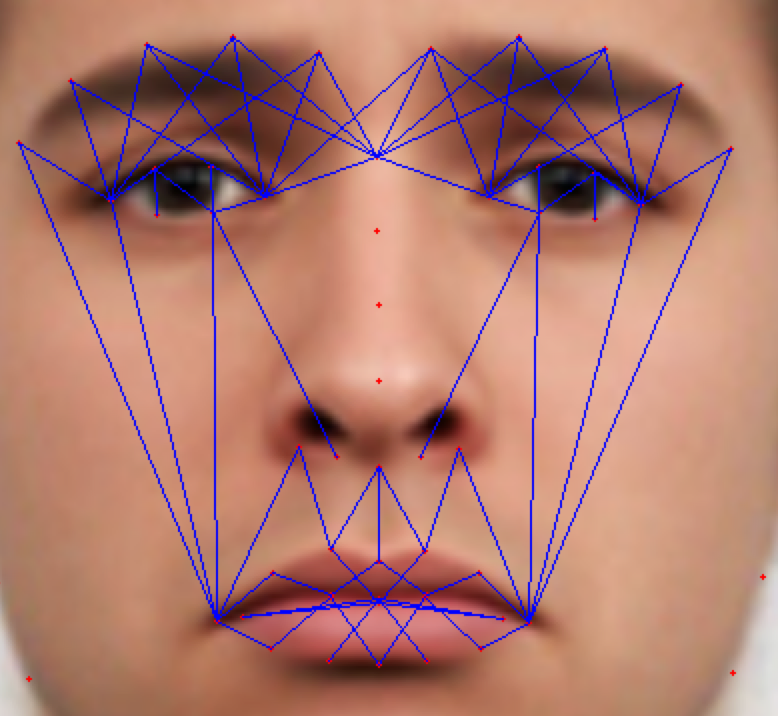
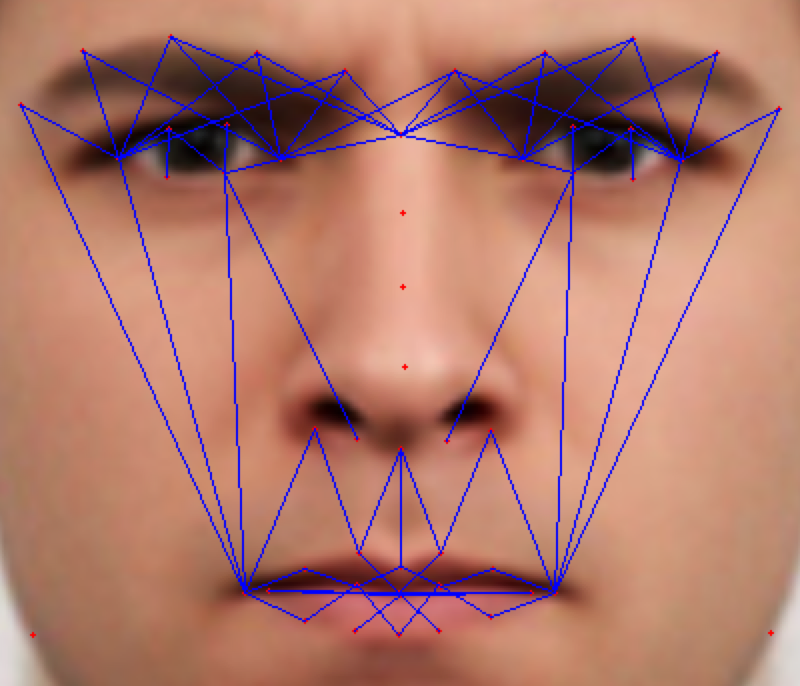
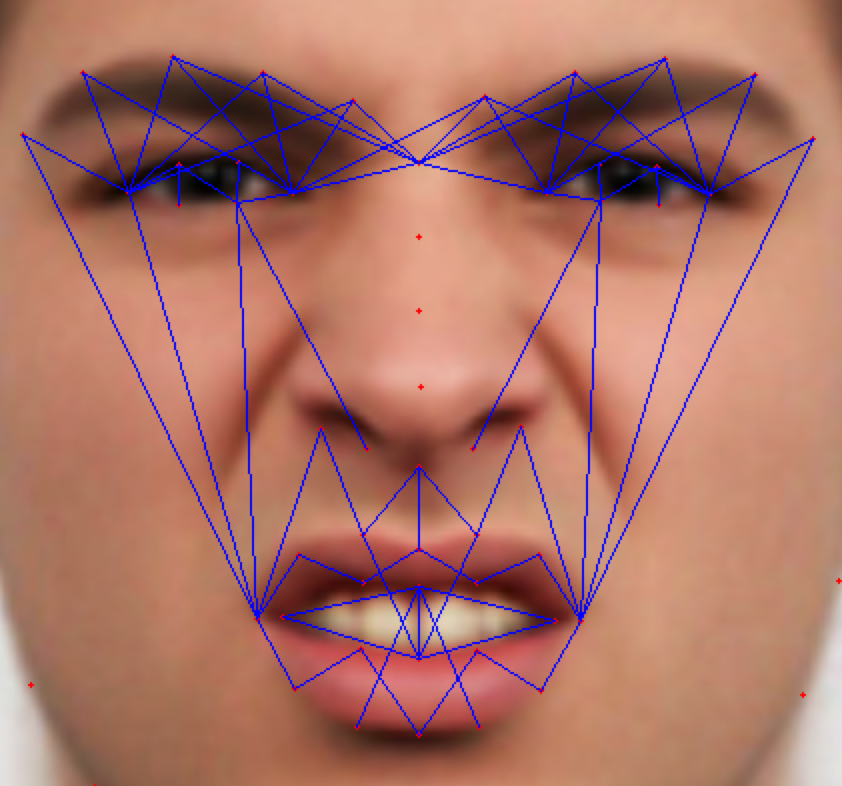
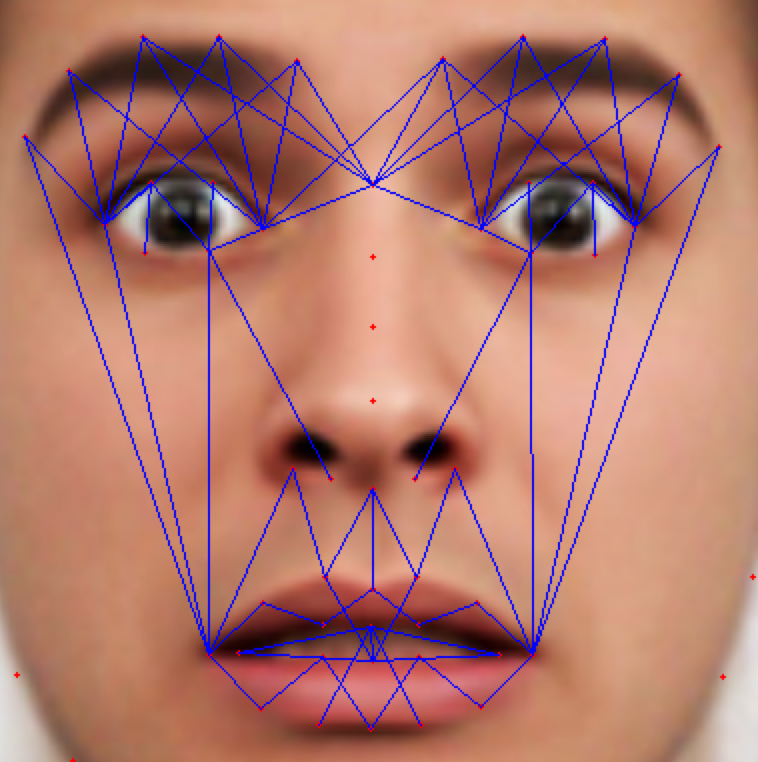
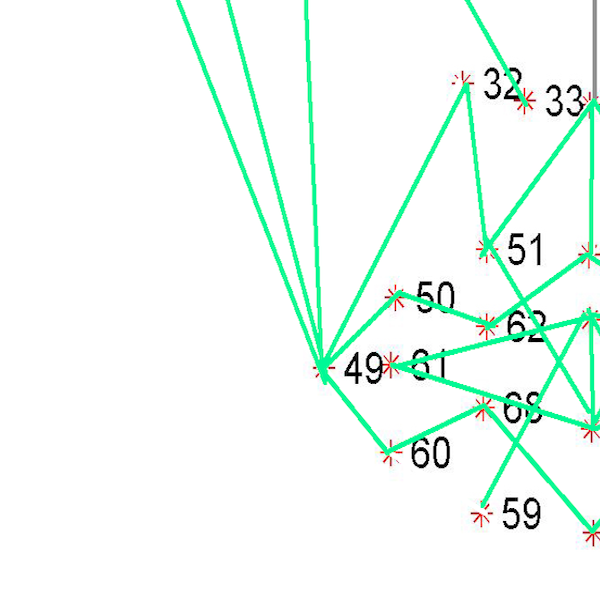
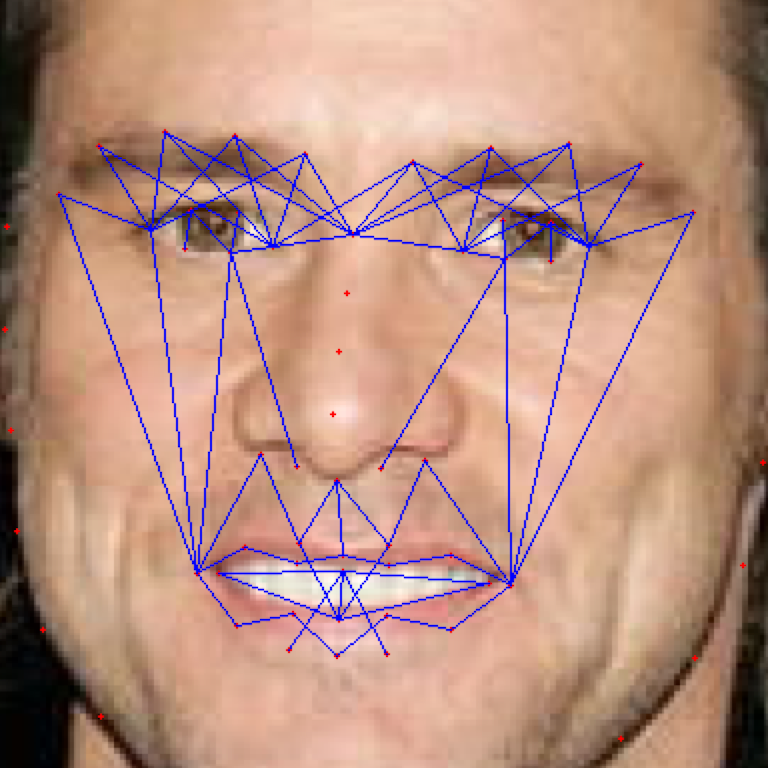
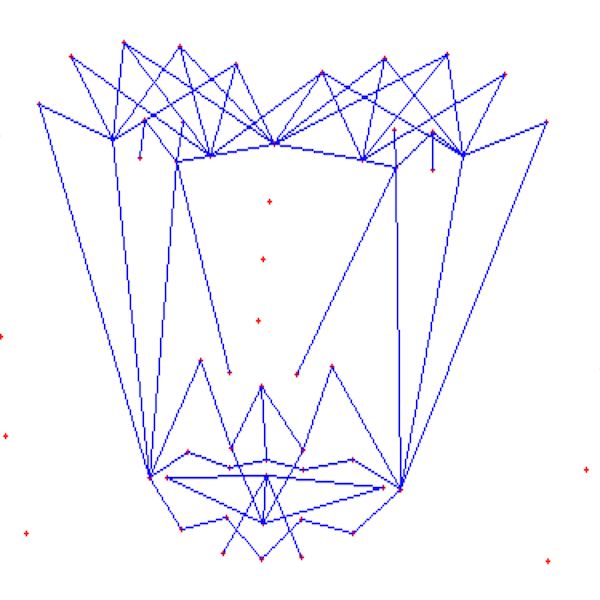
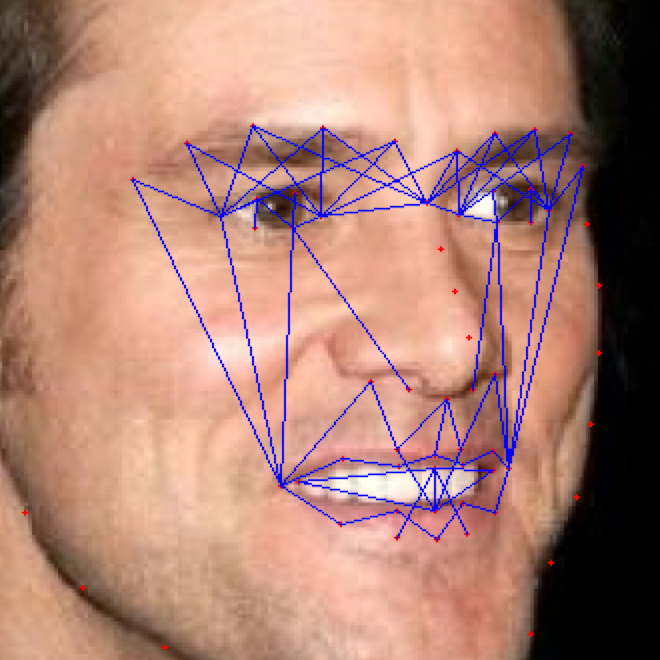
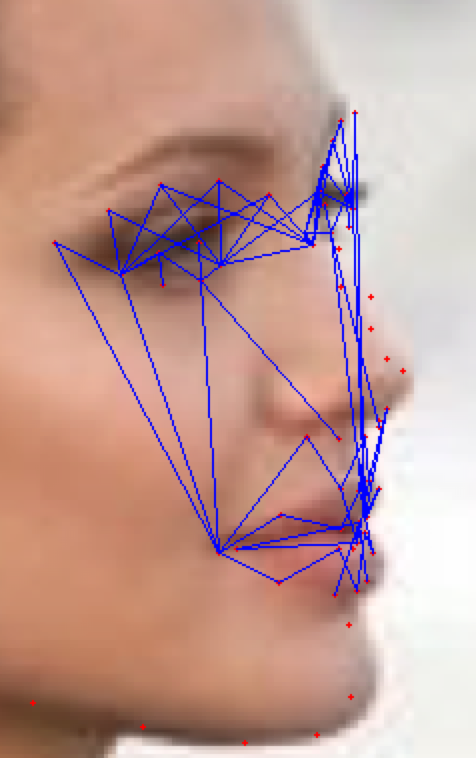
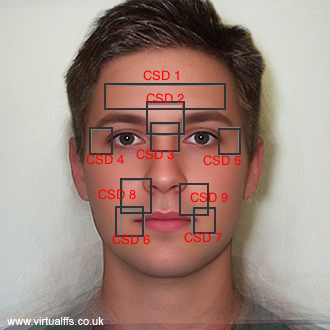
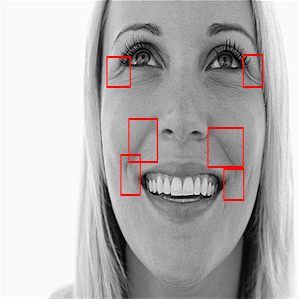
As the classification is carried into 5 prime emotions (and neutral), extracting key facial features is sufficient. To determine the feature vectors form the detected face frame, we plot **facial landmarks** over the face using AAM along with Lucas – Kanade (LK) algorithms. The facial landmarks are used to develop a **wireframe** across the face called as **mask**. The details are extracted from the mask, as facial feature vectors. The mask is scientifically designed to fulfill multiple challenges.
The most important phase which gives the model a new shape by increasing its accuracy, reducing runtime and makes it valid across different test cases, exceptions, etc. is facial feature extraction using values of angles between wireframe. It eliminates the need for pre-processing and facial alignment at a vast level and brings uniformity across the images. As upon processing the angles between wireframes don't change with the change in face alignment, shape, size, rotation(3D & 2D), etc.
To learn from facial skin textures (wrinkles) we implement a simple **HOG-LBP and Gabor-LBP cascades** near key landmark points.
An approximate but accurate enough, neutral expression mesh is generated for the same face detected using the " **Golden Ratios**". The driving forces are calculated between the "expressive mask" and "neutral mask". The driving forces, as well as the independent facial features of the expressive frame, are combined in a list to form Feature Vectors List. The list is traversed across the following Xgboost Classifier to get the predicted emotion.
These feature vectors can be clustered together representing various unique face actions called as " **Action units**". The combinations of these Action Units helps to predict different emotions.
The feature vectors are traversed across the **first level Xgboost** to determine the Action Units (AUs) of the corresponding expression sequences. Finally, the detected AUs are traversed across the **second level Xgboost** for facial expressions classification.
In parallel, another **Xgboost** model will classify emotion directly from feature vectors. The fused result gives us an accurate prediction.
The model is trained with a sequence of expression frames starting with less expressive to most expressive. Thus, face with any intensity of expression can be classified easily.
## Methodology:
1. Image frame retrieved from RPi_Cam_Web_Interface sent from Learnbot's camera in real – time.
2. The cascades are used for detecting faces and cropping (into 64 x 64).
(frontal to profile view in 3D)
3. The face is to grayscale and applying cv.createCLAHE tuner.
4. Facial Landmarks are positioned across the face using AAM and further dynamically re - localized using Lucas – Kanade method.
5. The face is masked with wireframes and feature vectors are extracted.
6. Parallel to step 5, a mask for neutral expression is generated based on "Golden Formula" and feature vectors are extracted. (Pose angle is estimated)
7. Multi – Cascade detectors are implemented in parallel to step 5 and 6
8. Force vectors are extracted from the masks and appended to the feature vectors list.
9. 1st fold Xgboost AU classifiers model (FACS) is used to determine probabilities of active Action Units.
10. 2nd fold Xgboost emotion classifier model is implemented to classify probability of emotion predicted based upon AUs activation probability.
11. Parallel, another Full-Emotion classifier is implemented to directly compute feature vectors to classify predicted emotions probability.
12. Probability results from both the models are combined to give a precise predicted emotion probability and label.
13. The result is then dynamically represented on screen graphically with necessary parameters.
## Foundation of the Model
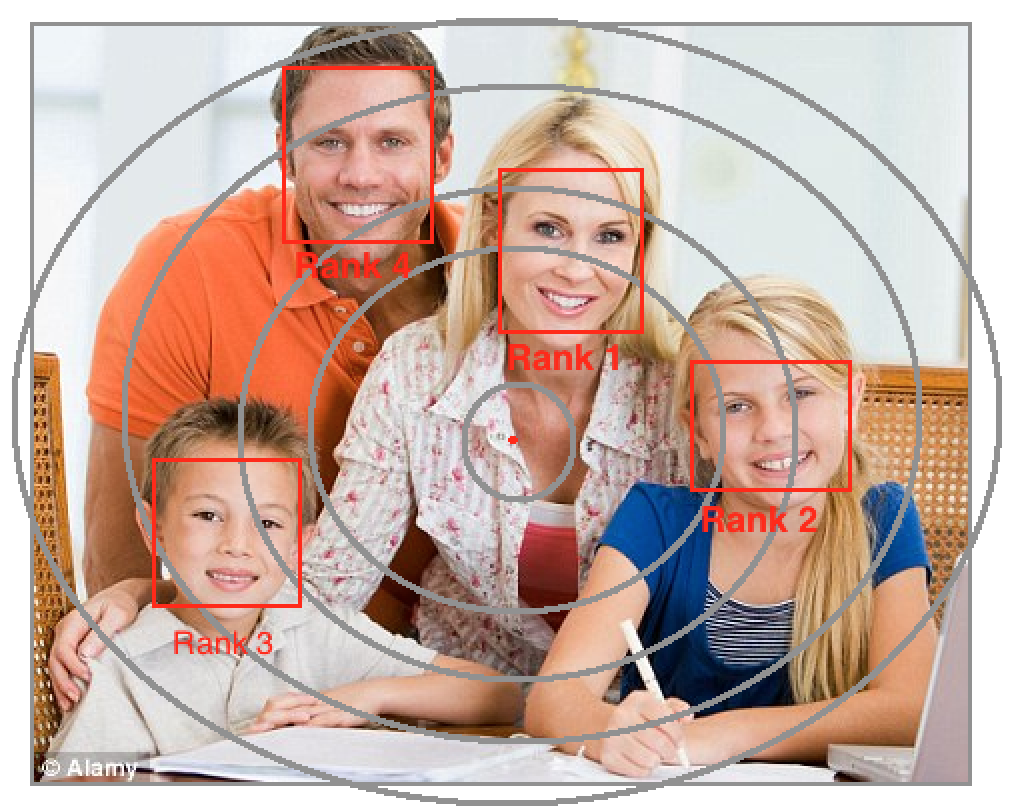
### Face Detection and Ranking:
The captured images using Learnbot's camera may contain one or more faces at a time. The whole frame is investigated using the Cascades for face detection from the front view to profile view. The face – rectangles then cropped are reshaped into 64 x 64 squares.
The face - rectangles are of different sizes and located at a different location across the frame based upon the position of human in front of Learnbot in 3D. These faces are assigned ranks as follows:
- **--** Ranking based upon the size of face-rectangle (measured diagonally) in descending order i.e., the larger rectangle is ranked prior to smaller ones. (seems to be near and more interactive)
- **--** Ranking based upon displacement from the center. A person at center should be prioritized.
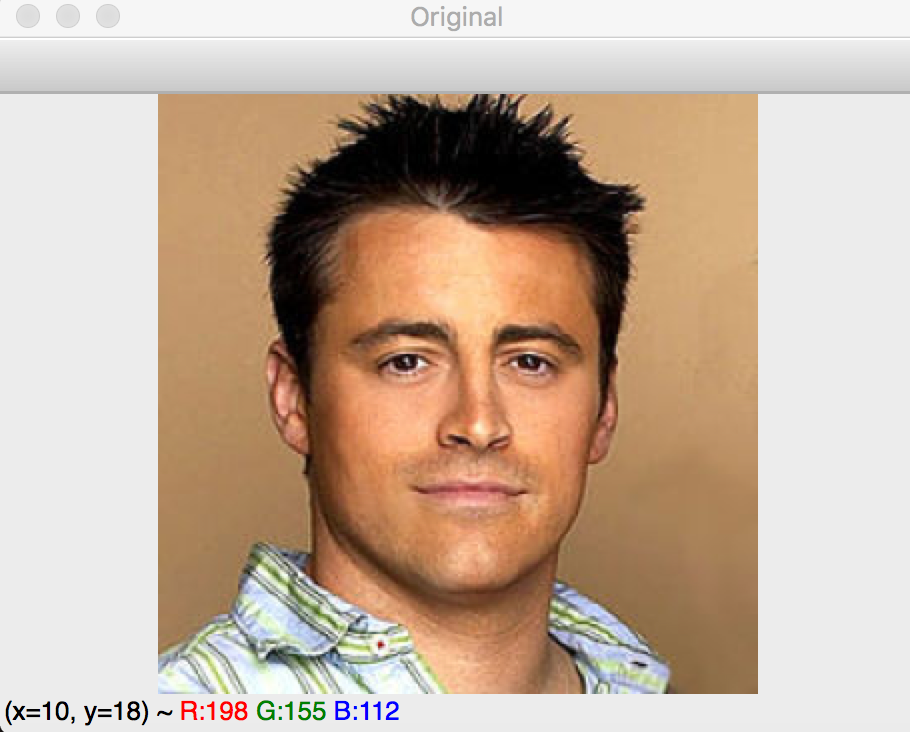
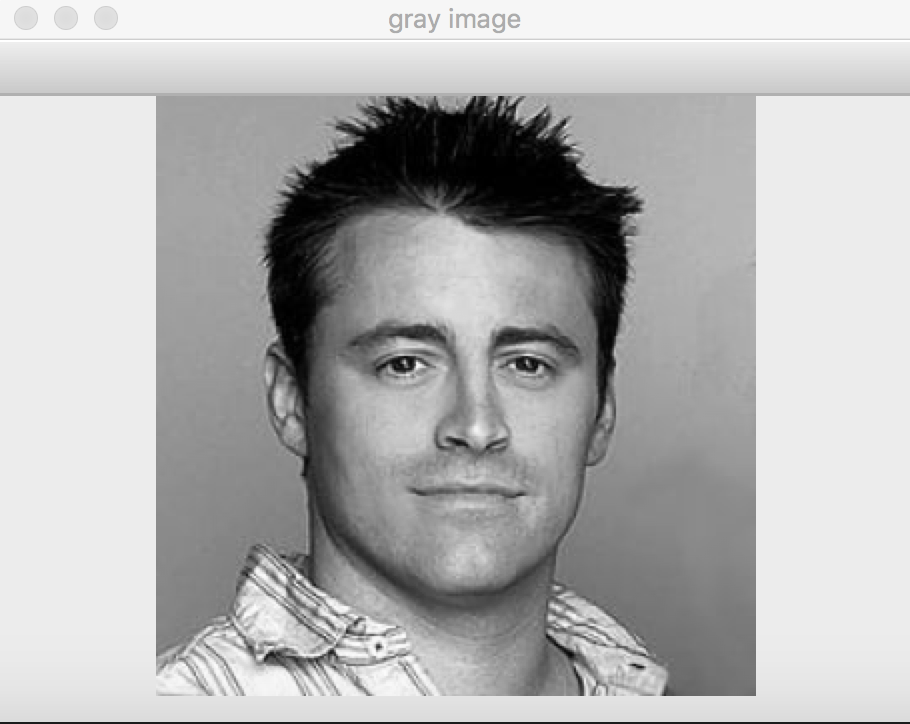
## Pre - Processing:
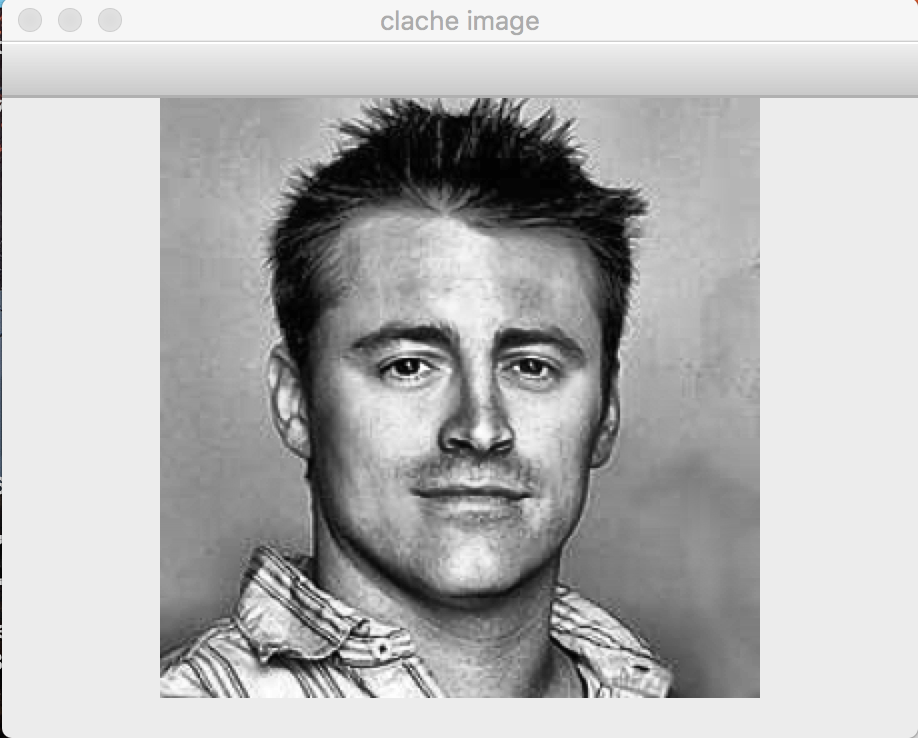
The face frame of 64 X 64 is then converted into grayscale from RGB form. It is then normalized and edges are sharpened by tuning OpenCV inbuilt function createCLAHE.
This is performed so that it reduces the runtime during skin texture detection and positioning of facial landmarks.
The model shows no requirement of any heavy or additional preprocessing and faces alignments, it works deals with the challenges more efficiently. (discussed in Masking).
Preprocessing: original image-->gray image-->clahe image
## Facial Landmarks:
Upon minimum pre-processing, the image becomes suitable to derive facial landmarks which could be further used to extract facial features.
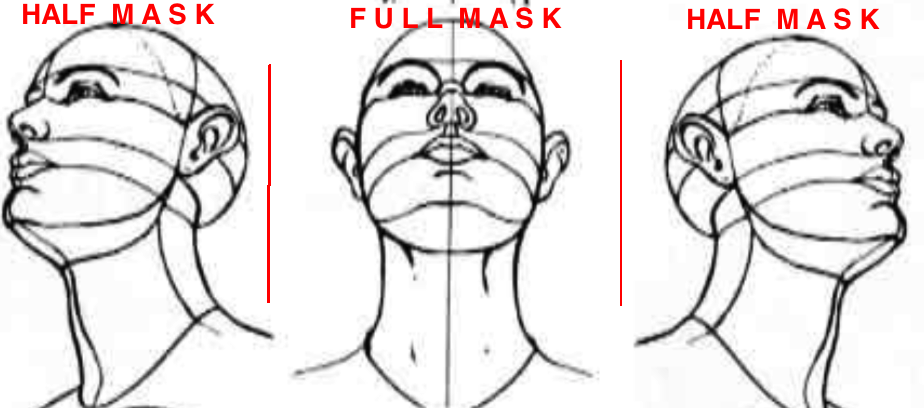
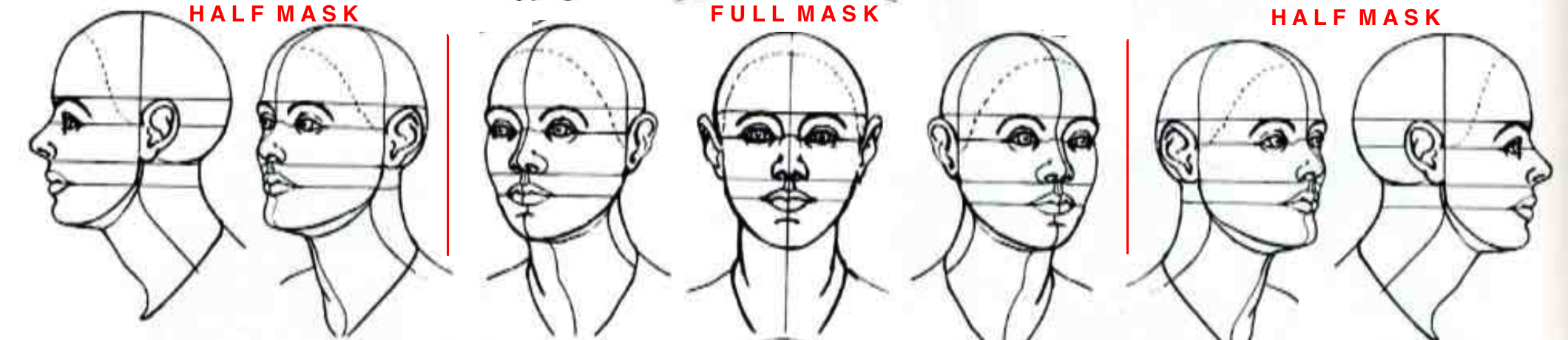
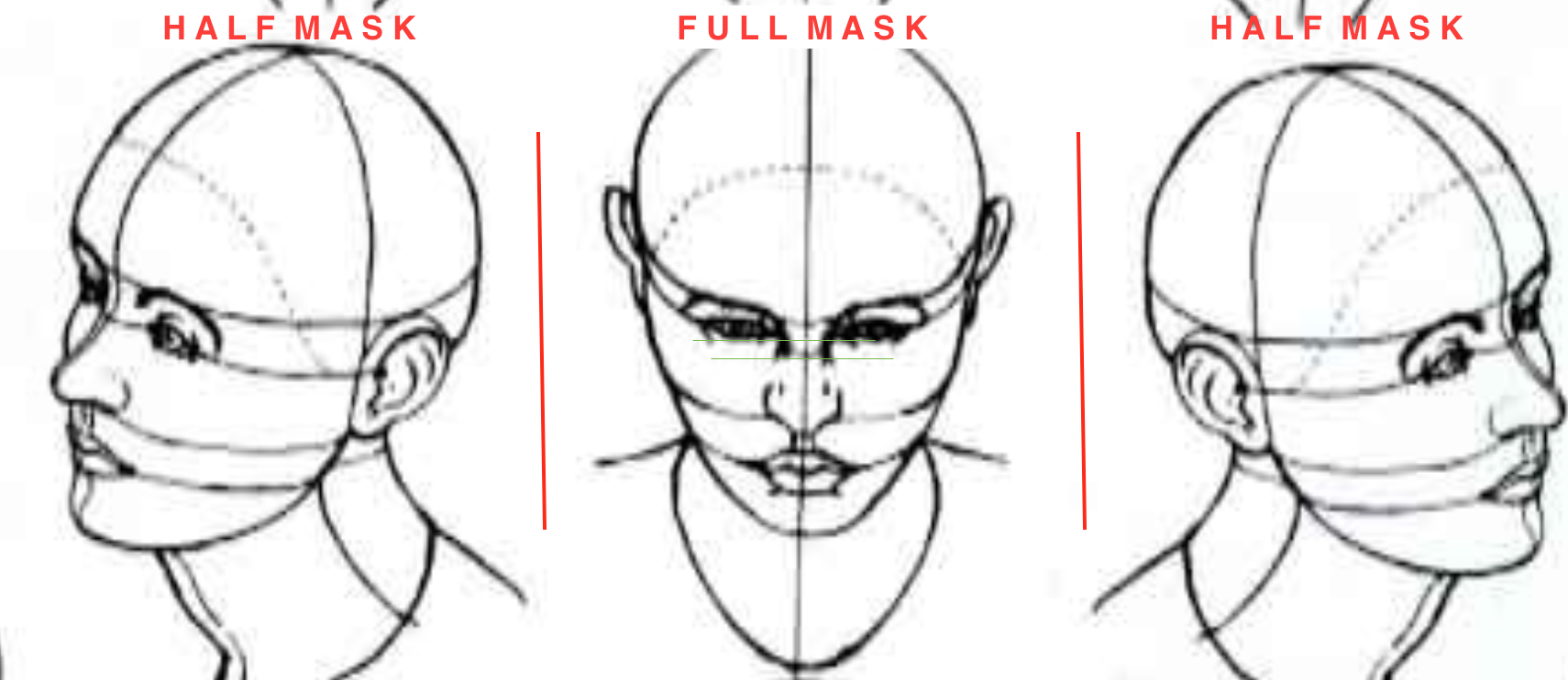
The facial landmarks are accumulated based upon pose of the face in XZ – plane and YZ – plane. So, we define a **threshold angle (alpha)** upto which the face is considered as " **Full-Face**" view and beyond it as " **Half- Face**" view. In case of Half-Face view only one half of face is used to determine the expression. The other half is either incapable of determining the exact landmark positions and distinguish among them or is not visible.
The initial frame landmarks are estimated using Active Appearance Model (AAM). An AAM face model consists a shape model and a texture model. The fitting procedure iteratively adjusts the model until satisfy.
Further in consecutive frames, Lucas–Kanade (LK) optical flow tracker can be used by estimating the displacements of the feature points.
## Face Masking:
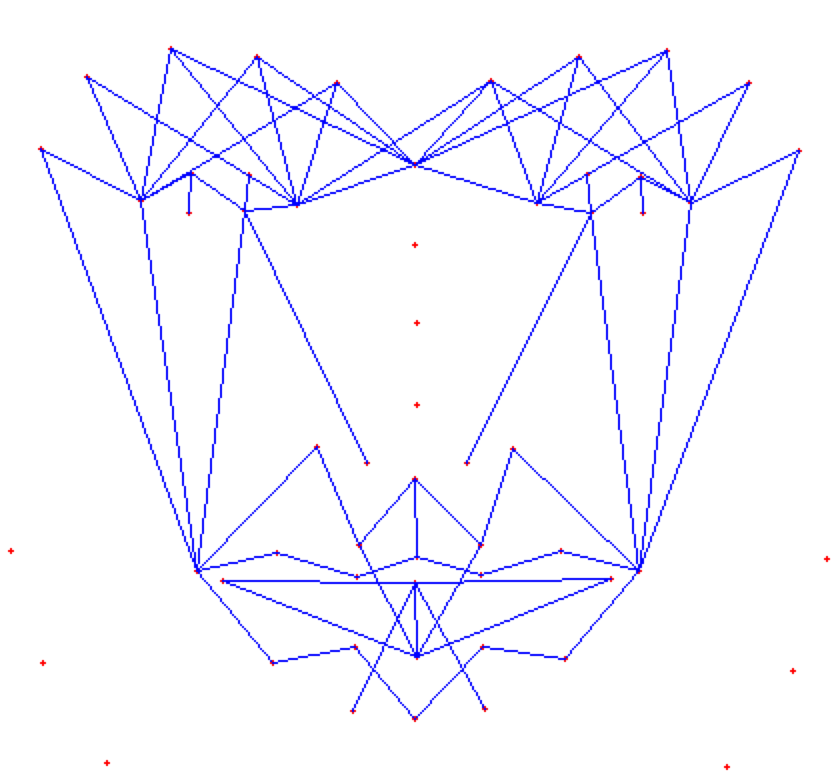
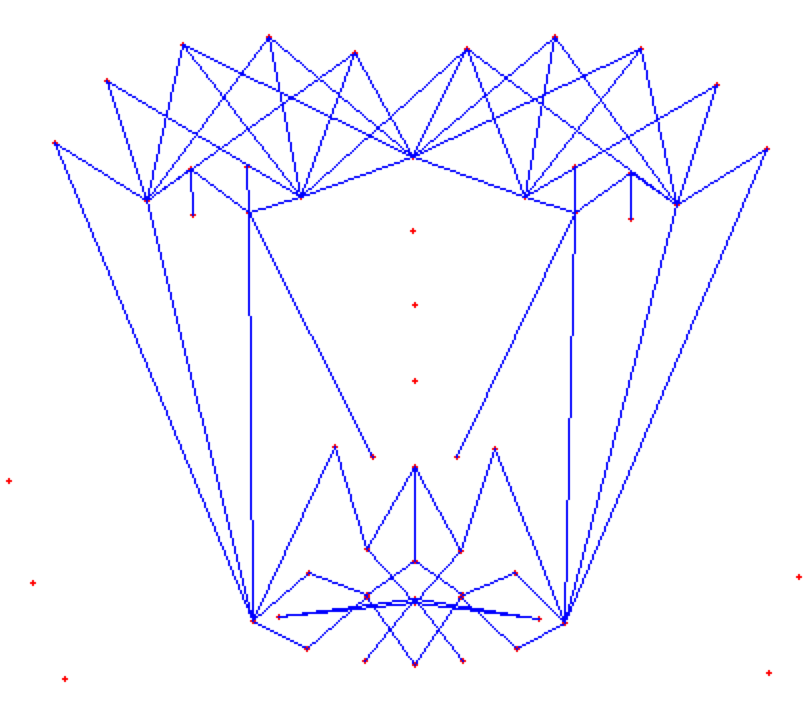
**(MOST IMPOTANT PHASE) (motivation:** **Candide Wireframe Model)**
The facial landmarks are very sensitive to the movements of facial muscles. Each person has unique face structure and gives vivid poses at different point of time. To study the pattern followed by vector displacement of these facial landmarks for any given expression, we generate mask over the face such that details extracted from them can be compared across the frames.
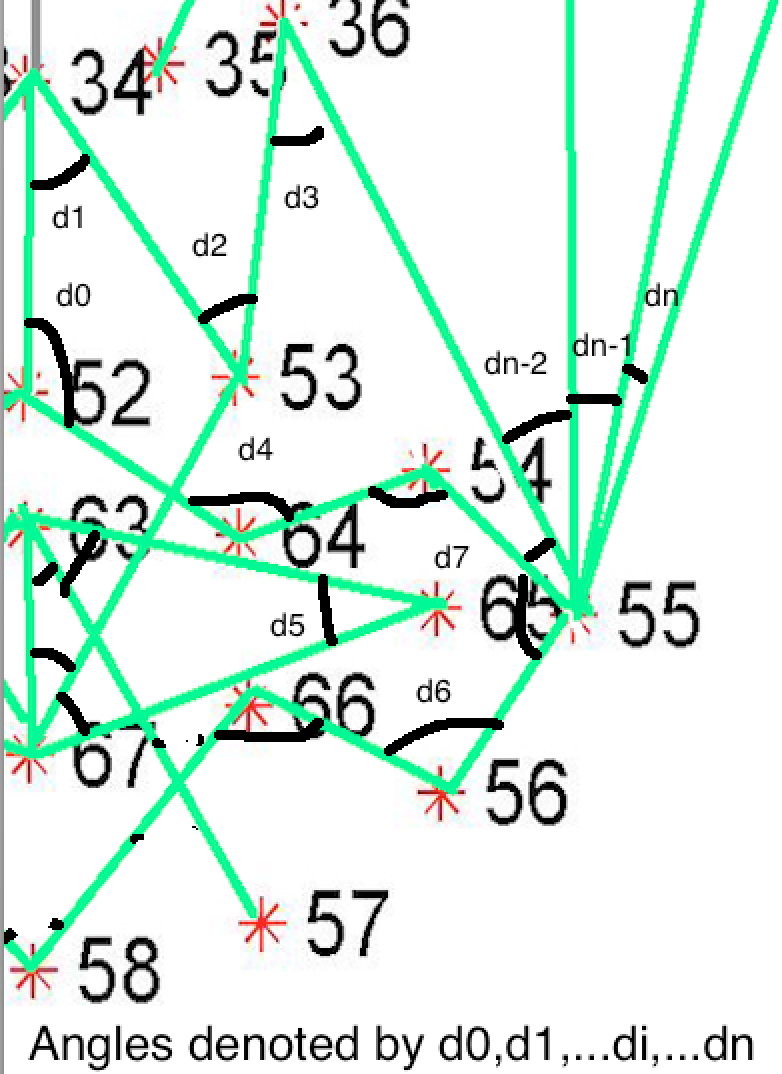
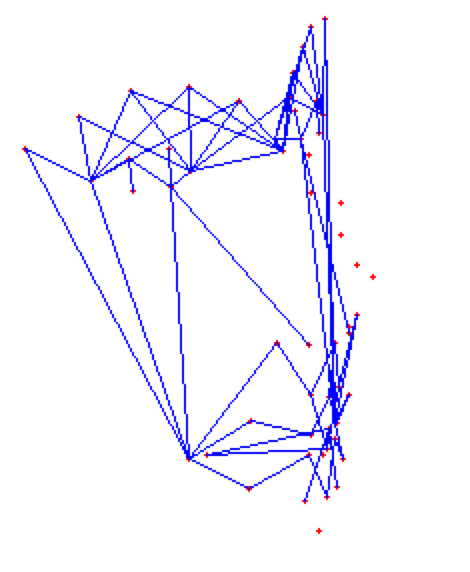
The architecture of the mask is motivated from **Candide Wireframe Model**. The driving forces exerted during the change in expression intensities are the distance between nodes and **angles at intersections in wireframe**.
The angles at intersections don't change with change orientation of face about z-axis or with any change in size (aspect ratio is constant) of the face frame for any given expression intensity.
Inorder to find the change in these driving forces we subtract the present frame mask's details with mask's details of neutral expression. The result is changed in terms of angles and displacements of nodes.
***Vector_final = Vector_expression - Vector_neutral***
To make it possible we first need to normalize the face within the frame and normalize the face across the frames.
**Normalization of feature vectors within the face frame:**
Face poses different angles in 3D, this leads to compression and expansion of angles within a face according to the degree of inclination.
Example:
Let, a person looks diagonally at an angle towards right-bottom. The angles between wireframes of left eyebrow will be relatively greater than right eyebrow's for same expression as compared to face at normal pose angles of same expression.
Thus,
***Feature Extraction:***
To avoid such variation within a frame, we can apply face-alignment to center. But, face-alignment of each frame will consume runtime (3D matrix) and don't gives the required solution. **So, we take a relative variation of the angle between wireframes for each feature within a frame and multiply by a constant value(like 10)** This solves the problem of any pose angles.
***Challenges solved:***
- The face can be posed in 2D or 3D, least alignment required
- Don't depend on size and shape of the face
**Normalization of feature vector across the faces frames:**
Every person has variations in the structure of the face. To determine the feature vectors of the face of an individual, we need their neutral expression dimensions, so that we can subtract neutral frame features from apex expression frame features of that person.
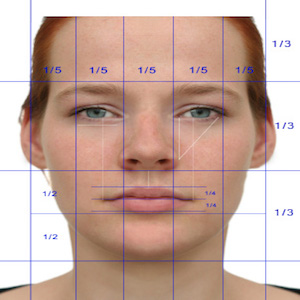
The neutral frame can be generated using Golden Ratio Formula. The generation of the whole mask for neutral expression is not required. We just need inner approximate aspect ratios(angles) of each feature of a face. And this can be computed very fast
using stable dimensions of the face in the frame i.e, the distance between an eye center and mid-point of both the eyes, the distance between mid-point of eyes and nose center and pose angle.
Only, the landmarks for eyebrows and lips are plotted using Golden Ratio, that too separately. So, there is no constraint of overlapping neutral mask generated with the actual person's mask.
Thus, masks are appropriate for classification into different expression classes.
**FULL MASK:**
If the front view of the face in the frame is visible clearly i.e., pose angle is less than or equal **threshold angle (alpha),** we use our full mask.
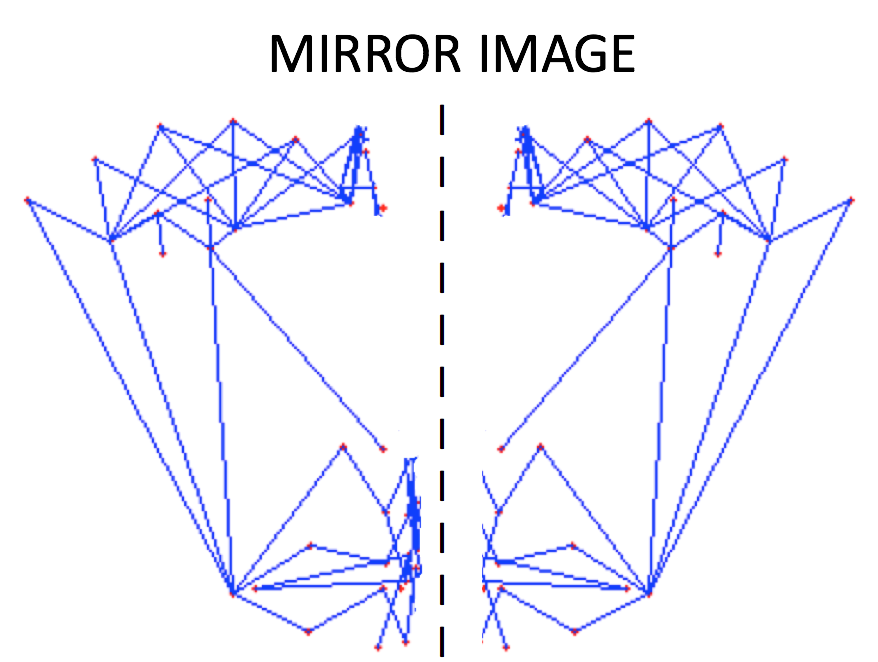
**HALF MASK:**
If the front view of the face in the frame is not clearly visible i.e., pose angle is greater than **threshold angle (alpha),** we use our half mask. ***The feature extracted from the one-half mask (suppose left view of the face) are replicated same as for the other half (mirroring).*** We calculate only for visible side and consider the same for both sides.
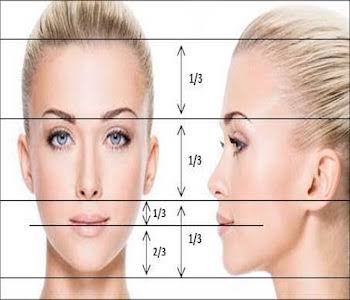
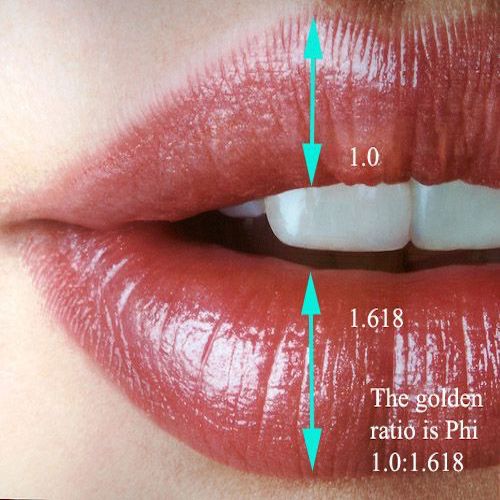
**Golden Ratio:**
Golden Ratio is a perfect fitting number. An ideal face is said to have feature positioned relatively based on this Golden Ratio and its derivatives.
There are variations in the shape and size of each facial feature (eyes, eyebrows, lips, nose, etc.), it's not necessary for the golden ratio to predict an exact neutral state of a face.
But, in our case **we don't need any exact shape, size or even relative position of features.** We just need an approximate constant value that can subtracted from the expression mask to normalise across frames which varies negligibly with across the frames.
It is just to bring faces with extremely different structures into comparable range. The relative position is not required between them, we just require inner approximate aspect ratio(angles) of a feature.
**Masks Driving Forces:**
## Multi - Cascade Detectors:
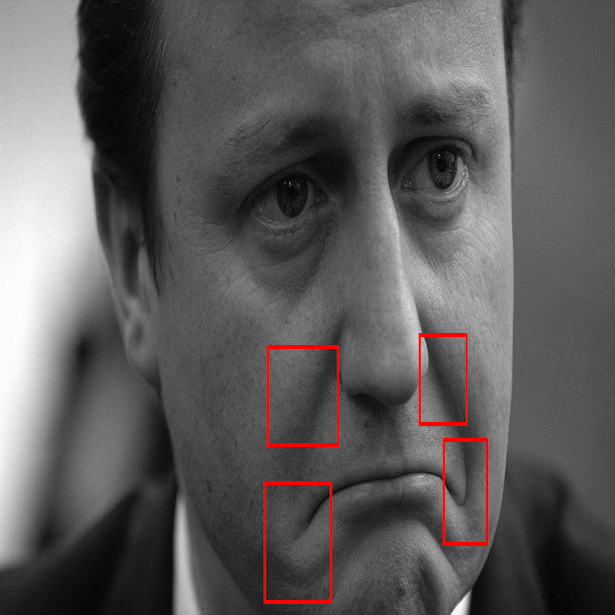
Some of the most important facial muscles show their movements in form of skin texture. These are the case where landmarks may not show drastic movements but the skin texture is enough to determine face expression features.
Skin textures can be examined at different regions of interest of the face using various "HOG LBP or Gabor LBP Cascades".
The cascades can be easily trained using OpenCV functions **opencv\_haartraining and opencv\_traincascade.**
The region of interst (ROI) is determined by their nearest landmarks' on the face. The output feature vectors derived using cascades are represented in form of binary {0,1}.
## AUs Xgboost (xgb\_1\_1):
The various face expression feature vectors can be clustered together, to define a cumulative muscle actions, called as Action Units. The classification is computed using xgboost algorithm. 17 AUs are to be recognized, they are AU1, AU2, AU4, AU5, AU6, AU7, AU9, AU12, AU14, AU15, AU17, AU20, AU23, AU24, AU25, AU27 and AU38. Out of these the following are particulars for valid emotion recognition.
A xgboost model is created where inputs are the face feature vectors, and the output is classified Action Units. The model tree is trained such that the combinations of a definite range of varying feature intensities are clustered under each Action Units. The model is called FACS.
We get required active AUs probabilities, classified based upon given feature vectors.
## Xgboost Classifier(xgb\_1\_2):
The second fold Xgboost model is based upon activeness of various AUs to classify an emotion. The classification is performed, by feeding probabilities of AUs active in a frame and computed output is the probabilities of emotions possibly shown.
## Full – Xgboost (xgb\_2):
Due to less accuracy in prediction of activeness of AUs, the final classification may lead to wrong predictions. Thus to overcome wrong predictions and get accurate probability distribution across emotions, we implement a model computing emotion classification directly by classifying feature vectors into emotion classes. The model runs in parallel to 2-fold Xgboost model.
## Fused Result:
The output probabilities of emotions from both the model are combined based upon the strength of each emotion relative to others from each model.
More the deviation in prediction probabilities from each model, the high chances of distinct and valid prediction. The maximum probability of the final output is our predicted emotion.
## Result Presentation:
The final predicted emotion’s probability is used to measure the intensity of the emotion. Moreover, it thus helps to classify the neutral state of emotion.
We take three layers to sub-classify the intensity of the emotion.
For example,
If only the two high probabilties conflict they give 50 as predicted probabilty. Thus, in stage 3 we are most confident with prediction and in stage 0, it's almost neutral or highly conflicting.
## Steps towards accuracy:
- **--** Similar face alignment across frames
- **--** Customising facial landmark positioning, and cascades as per emotion-faces and pose angles
- **--** Proper selection of feature vectors
- **--** Perfect masking
- **--** Accuracy can be gained further by tuning of the Xgboost models
**Thank You**
**References:**
1. Xiaorong Pu, Ke Fan, Xiong Chen, Luping Ji, Zhihu Zhou, Facial expression recognition from image sequences using twofold random forest classifier, Neurocomputing, Volume 168, 2015, Pages 1173-1180, ISSN 0925-2312,
link: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925231215006220
2. Facial Action Coding System (FACS) – A Visual Guidebook: https://imotions.com/blog/facial-action-coding-system/
3. Kotsia I, Pitas I, Facial Expression Recognition in Image Sequences Using Geometric Deformation Features and Support Vector Machines
link: http://sci-hub.tw/http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/4032815/
4. Golden Ratio: https://www.goldennumber.net/golden-ratio-design-beauty-face-evidence-facts/#jp-carousel-8098
5. Packiriswamy V, Kumar P, Rao M, Identification of Facial Shape by Applying Golden Ratio to the Facial Measurements: An Interracial Study in Malaysian Population, N Am J Med Sci. 2012 Dec; 4(12): 624–629. doi: 10.4103/1947-2714.104312
link: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3530317/
6. Candide Face Masking: http://www.icg.isy.liu.se/candide/
** **